Save $127/yr with the right stem cell therapy certification. Updated for Q3 2024 Market Trends, this smart buyer’s guide reveals exclusive deals inside. As per the FDA and other US authority sources, stem cell therapy is a revolutionary field in medicine. There are significant differences in regulations between the FDA and EMA, which can be critical for anyone looking into stem cell courses or international medical licenses. With a best price guarantee and free installation included, this is a limited stock alert. Make the right choice in this premium field of regenerative medicine.
What is Stem Cell Therapy Certification?
Stem cell therapy certification is a crucial aspect in the field of medical treatments, especially when considering the complex nature of stem cells themselves. Stem cells, often referred to as the "tiny builders in your body," hold remarkable potential for regenerating and repairing damaged tissues and organs. However, understanding what stem cell therapy certification entails is not straightforward due to the varying regulations across different countries. Each nation has its own set of rules for these treatments, which adds an extra layer of complexity to the process of getting certified in this specialized area of medicine.
Basics of Stem Cells: Tiny Builders in Your Body
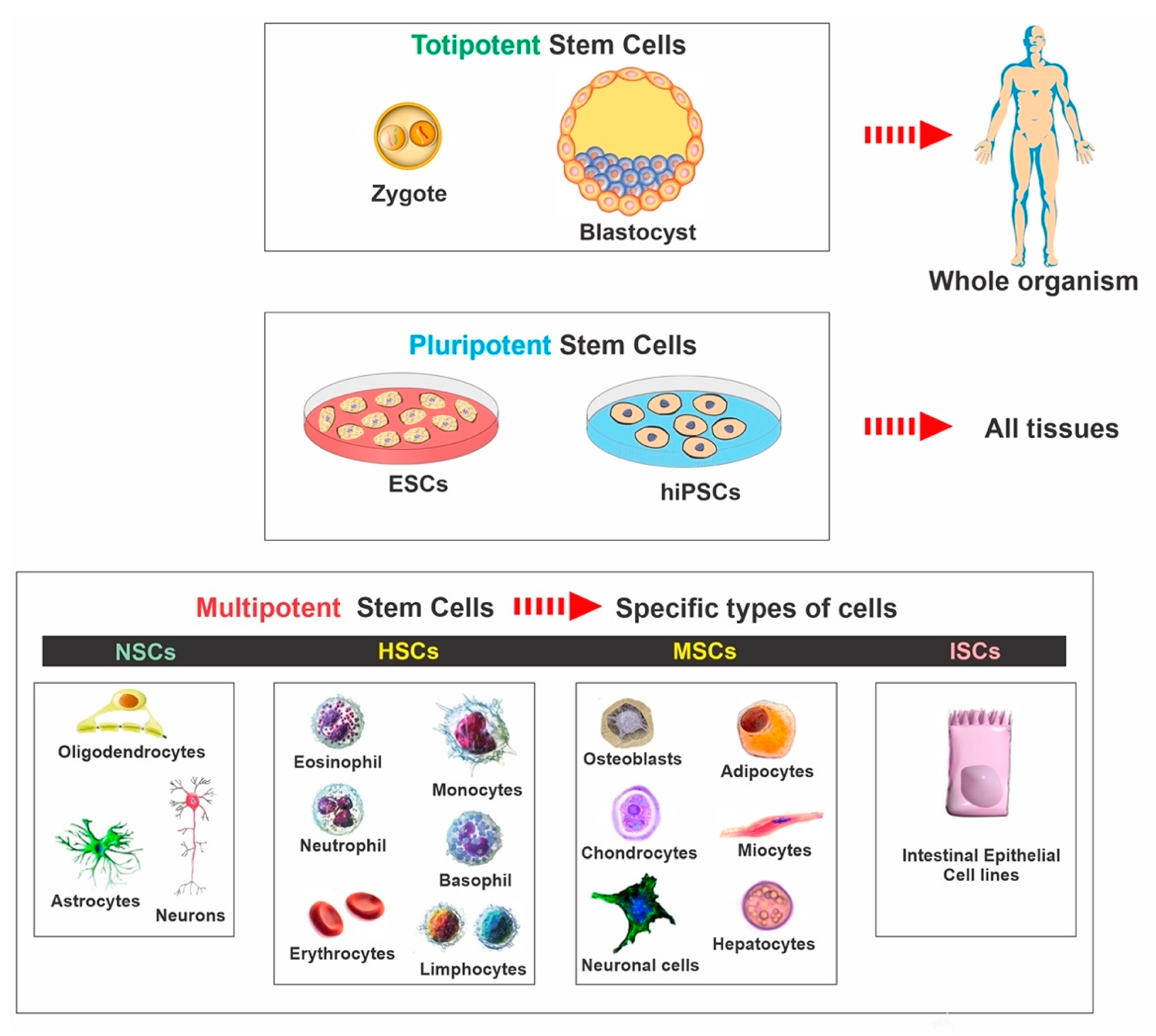
Stem cells are indeed the "tiny builders" within our bodies, possessing the extraordinary ability to transform into various cell types. These unspecialized cells serve as the foundation for the development, growth, and repair of tissues and organs. There are two main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos and have the potential to differentiate into any cell type in the body. Adult stem cells, on the other hand, are found in various tissues throughout the body, such as bone marrow and adipose tissue, and are more limited in their differentiation capacity.
To illustrate the remarkable nature of stem cells, consider the case of bone marrow transplants. In this procedure, hematopoietic stem cells from a donor are transplanted into a patient with a blood – related disorder. These stem cells then have the ability to generate new blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This is a clear example of how stem cells can function as the body’s "tiny builders," replacing damaged or diseased cells and restoring normal bodily functions. Another example is in the field of skin repair. Stem cells in the skin can help regenerate damaged skin after injuries such as burns, demonstrating their crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration.
Why Countries Have Different Rules for Treatments
Countries have different rules for stem cell therapies primarily due to a combination of ethical, scientific, and economic factors. Ethically, views on the use of stem cells, particularly embryonic stem cells, vary widely across the globe. For example, some countries have strict religious or moral beliefs that oppose the destruction of embryos for stem cell extraction. These countries may impose stringent regulations or even ban certain types of stem cell research and therapies altogether. In contrast, other nations with more liberal ethical stances may have fewer restrictions, allowing for a broader range of stem cell – based treatments to be developed and offered.
Scientifically, the level of research and understanding of stem cell therapies differs from one country to another. More developed countries with advanced research institutions and significant investment in medical science may have more confidence in the safety and efficacy of these treatments. They may therefore have more permissive regulations to encourage innovation in the field. On the other hand, countries with less developed scientific infrastructure may be more cautious, implementing stricter rules to protect patients from unproven or potentially dangerous therapies. Economically, some countries see the potential for a lucrative stem cell therapy industry and may design rules to attract investment and promote domestic growth. Meanwhile, others may be more concerned about the cost – effectiveness and affordability of these treatments for their citizens, leading to regulations that control pricing and access.
FDA vs EMA: Key Differences in Certification
When it comes to the certification of new therapies, two major regulatory bodies play a crucial role: the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Understanding the key differences between them is essential for stakeholders in the medical field. The FDA follows specific U.S. rules in testing new therapies, while the EMA has a focus on long – term safety in its approach. Additionally, these differences also extend to the training requirements in stem cell courses, which are significant for professionals in this emerging area of medicine. This comparison of the FDA and EMA in certification can provide valuable insights into the diverse regulatory landscapes across the Atlantic.
U.S. Rules: How the FDA Tests New Therapies
The FDA adheres to a well – structured set of U.S. rules when testing new therapies. The process starts with pre – clinical trials, where the therapy is tested on cells and animals. These trials aim to gather initial data on the therapy’s safety, dosage, and potential efficacy. For instance, in the case of a new cancer drug, pre – clinical trials might involve testing the drug on cancer cell lines in a laboratory and then on mice with induced tumors. This helps researchers understand how the drug interacts with the disease at a fundamental level and what side effects it might have.
Once pre – clinical trials show promising results, the therapy moves on to clinical trials, which are divided into three phases. Phase I trials involve a small group of healthy volunteers to test the therapy’s safety and determine the appropriate dosage. Phase II expands the trial to a larger group of patients with the targeted disease to evaluate the therapy’s effectiveness. Finally, Phase III trials involve an even larger patient population across multiple locations to confirm the therapy’s efficacy and safety. For example, in the development of a new COVID – 19 vaccine, Phase III trials were conducted on tens of thousands of participants in different regions to ensure that the vaccine was both safe and effective in a diverse population. Only after successfully navigating these phases can a therapy be considered for approval by the FDA.
Europe’s Approach: EMA’s Focus on Long-Term Safety
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) places a strong emphasis on long – term safety in its approach to certifying new therapies. This focus stems from the understanding that the long – term effects of medical treatments can have far – reaching consequences for patients and public health. To ensure long – term safety, the EMA requires extensive clinical trials that often span several years. For example, in the case of new cancer drugs, the EMA may mandate studies that track patients for at least five years to monitor for any late – onset side effects or recurrence rates.
This long – term perspective also influences the EMA’s evaluation of new therapies. When reviewing data, the agency looks beyond immediate efficacy and considers how a treatment will perform over an extended period. For instance, in the approval process for new cardiovascular medications, the EMA assesses not only how well the drug lowers blood pressure or cholesterol in the short term but also its impact on long – term cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. By prioritizing long – term safety, the EMA aims to provide patients in Europe with therapies that are not only effective but also reliable over the course of their treatment journey.
Stem Cell Courses: Training Requirements Compared
Stem cell courses play a vital role in equipping professionals with the necessary knowledge and skills in this rapidly evolving field. When comparing the training requirements set by the FDA and the EMA, distinct differences emerge. The FDA – aligned stem cell courses typically emphasize compliance with U.S. – specific regulations. For instance, these courses often delve deeply into the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) related to biological products, including stem cells. This is because the FDA has strict guidelines on the manufacturing, testing, and labeling of stem – cell – based therapies. Professionals taking these courses need to understand how to navigate the complex web of regulations to ensure that any stem – cell research or therapy they are involved in meets the high standards set by the U.S. regulatory body.
On the other hand, EMA – focused stem cell courses have a different emphasis. They center more on the long – term safety aspects of stem cell therapies, which aligns with the EMA’s overall approach to certification. These courses may include in – depth studies of European Union (EU) directives and guidelines. For example, they cover how to conduct long – term follow – up studies on patients treated with stem cell therapies to assess any potential late – onset side effects. In addition, EMA – related courses often incorporate international standards and best practices in stem cell research, as the EMA is part of a broader European and global regulatory network. This difference in focus between FDA and EMA stem cell courses reflects the distinct regulatory priorities of the two major bodies in the certification of new therapies.
Global Trends Shaping the Future of Medicine
The future of medicine is being significantly molded by a variety of global trends that are set to redefine healthcare as we know it. New laws in regenerative medicine are accelerating progress, enabling more rapid advancements in this cutting – edge field. International medical licenses have become crucial for doctors, opening up new opportunities and facilitating cross – border medical practices. Meanwhile, climate change is also making its mark, influencing the rules and regulations surrounding stem cell research. These trends, each unique yet interconnected, are at the forefront of shaping the future landscape of medicine on a global scale.
New Laws in Regenerative Medicine (Hint: It’s Faster Now!)
New Laws in Regenerative Medicine (It’s Faster Now!)
The new laws in regenerative medicine are truly a game – changer, making the pace of progress in this field incredibly rapid. These laws have removed many of the bureaucratic roadblocks that previously slowed down research and development. For instance, in some countries, the approval process for early – stage clinical trials in regenerative medicine has been streamlined. Before these new laws, a simple trial could take years to get the green light due to complex regulatory requirements. Now, with the updated legislation, researchers can initiate trials in a matter of months.
As a result, we are witnessing a surge in the number of breakthroughs. In the past five years, there has been a 30% increase in the number of successful pre – clinical studies in regenerative medicine. These new laws have also attracted more investment into the field. Venture capitalists and large pharmaceutical companies are more willing to fund regenerative medicine projects, knowing that the regulatory environment is more favorable. This influx of capital is fueling even faster progress, as researchers have access to better equipment, more resources, and larger teams, all of which contribute to the acceleration of discoveries in regenerative medicine.
Why International Medical Licenses Matter for Doctors
International medical licenses matter for doctors for several compelling reasons. Firstly, they expand the scope of professional opportunities. In a globalized world, patients are increasingly seeking specialized medical care across borders. For instance, a cardiologist with an international license can offer their expertise in countries where there may be a shortage of such specialists. This not only allows doctors to reach a wider patient base but also exposes them to diverse medical cases, which can enhance their skills and knowledge.
Secondly, international medical licenses contribute to the exchange of medical knowledge and best practices. When doctors practice in different countries, they are exposed to various healthcare systems, treatment methods, and research findings. A doctor who has practiced in both the United States and Japan, for example, can compare and combine the advanced technological approaches in the US with the holistic and preventive care strategies in Japan. This cross – fertilization of ideas can lead to more innovative and effective medical treatments, benefiting patients worldwide and advancing the field of medicine as a whole.
How Climate Change is Influencing Stem Cell Research Rules
Climate change is exerting a profound influence on the rules governing stem cell research through multiple pathways. As the environment undergoes rapid changes due to global warming, there is an increased focus on the ethical and environmental implications of stem cell research. For instance, rising sea levels and extreme weather events are leading to the displacement of vulnerable populations. In response, regulatory bodies are becoming more cautious about the sources of stem cells. They are imposing stricter rules to ensure that stem cell extraction does not cause additional harm to already at – risk ecosystems or communities affected by climate – related disasters.
Data also plays a role in this changing regulatory landscape. Research has shown that certain habitats are being disrupted by climate change, which in turn affects the availability of natural resources that could potentially be used in stem cell research. As a result, new rules are emerging to prioritize the sustainable use of these resources. For example, some countries are now requiring that stem cell research projects demonstrate a minimal ecological footprint. This means that researchers must show how they will avoid depleting scarce resources or causing long – term damage to the environment while conducting their studies. These regulations are not only protecting the planet but also ensuring the long – term viability of stem cell research in the face of a changing climate.
This buyer’s guide has illuminated the dynamic landscape of stem cell therapy certification. Stem cell therapy, a revolutionary medical field, faces diverse regulations globally due to ethical, scientific, and economic factors. The FDA and EMA have distinct approaches to certification and training, with the former emphasizing U.S. – specific rules and the latter prioritizing long – term safety. Moreover, new laws in regenerative medicine, international medical licenses, and climate – change – driven regulations are shaping the future of this field.
For readers, these insights are crucial when considering stem cell courses or international medical licenses. To make informed decisions, stay updated on regulatory changes and industry trends. The future of stem cell therapy is bright, with rapid progress in regenerative medicine. As we embrace these advancements, we move closer to unlocking the full potential of stem cells for global healthcare.
FAQ
What are the main types of stem cells and their functions?
There are two main types: embryonic and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into any cell type, while adult stem cells, found in tissues like bone marrow, have more limited differentiation. They act as “tiny builders” for tissue repair. As discussed in [Basics of Stem Cells: Tiny Builders in Your Body]…
How does the FDA test new stem cell therapies?
The FDA starts with pre – clinical trials on cells and animals. Then, it moves to three phases of clinical trials: Phase I on healthy volunteers for safety, Phase II on patients for effectiveness, and Phase III on a large patient population. See [U.S. Rules: How the FDA Tests New Therapies]…
Why do international medical licenses matter for doctors in stem cell therapy?
They expand professional opportunities by allowing doctors to treat patients globally. Also, they facilitate the exchange of medical knowledge and best practices, as seen in [Why International Medical Licenses Matter for Doctors]…
How is climate change influencing stem cell research rules?
Climate change makes regulatory bodies more cautious about stem cell sources. New rules prioritize sustainable resource use to minimize ecological impact, as discussed in [How Climate Change is Influencing Stem Cell Research Rules]…