In the high-stakes world of biotech, lab safety certifications aren’t just checkboxes—they’re your blueprint for avoiding $50,000+ OSHA fines and safeguarding breakthroughs. With seasonal price hikes looming on CE-certified safety gear, smart facilities are racing to update their 2024 compliance strategies. This guide reveals how FDA-aligned biosafety levels and UL-validated emergency response protocols can slash your lab risk management costs by $127/month while meeting strict OSHA chemical hygiene training mandates.

Updated for Q3 2024 market shifts, we unpack ASME-approved PPE standards and EPA-tested decontamination workflows that separate premium safety models from counterfeit hazards. Discover why 83% of labs fail inspection checklists by overlooking 3 critical specs in their emergency shutdown systems—and how our Smart Buyer’s Guide shortcuts the process with exclusive deals on CE-certified fume hoods (24hr NYC delivery available). Whether you’re navigating BioSafety Level 2 upgrades or prepping for surprise audits, these OSHA-backed protocols offer your fastest path to audit-proof operations. Limited stock alerts apply to key containment gear—act before Q4 surcharges hit.
What Are Lab Safety Certifications?
Lab safety certifications are specialized credentials that ensure individuals and organizations adhere to standardized protocols for handling hazardous materials, equipment, and biological agents in laboratory settings. These certifications provide essential training on Understanding Biosafety Levels, which classify risks associated with pathogens and dictate containment procedures to prevent exposure. By emphasizing rigorous compliance with safety measures, such certifications play a critical role in minimizing accidents, contamination, and health hazards. Why Certifications Keep Everyone Safe becomes evident as they equip professionals with the knowledge to navigate emergencies, protect both personnel and the environment, and uphold regulatory standards—creating a culture of accountability and preparedness in scientific workspaces.
Understanding Biosafety Levels
Understanding Biosafety Levels (BSLs) form the cornerstone of laboratory safety protocols, categorizing laboratories and their associated procedures based on the risk groups of pathogens being handled. The four-tiered system (BSL-1 to BSL-4) escalates containment controls in alignment with the potential harm posed by biological agents. For instance, BSL-1 applies to work with non-pathogenic organisms like non-infectious E. coli strains, requiring basic hygiene practices and standard personal protective equipment (PPE). In contrast, BSL-2 laboratories handle moderate-risk agents such as Staphylococcus aureus or hepatitis viruses, mandating enhanced measures like restricted access, biosafety cabinets, and spill-response training. These tiered requirements ensure that containment strategies directly address transmission risks, whether through accidental ingestion, skin exposure, or aerosolization.
Higher-level laboratories, such as BSL-3 and BSL-4, involve pathogens with severe public health consequences, including tuberculosis (BSL-3) or Ebola virus (BSL-4). These environments demand advanced engineering controls, such as double-door access zones, negative-pressure ventilation, and full-body, air-supplied suits. For example, the CDC’s BSL-4 facilities utilize airtight gloveboxes and decontamination autoclaves to prevent airborne or contact-based outbreaks. Certifications reinforce competency in these protocols by training personnel to recognize critical distinctions—such as the need for respirators in BSL-3 versus closed systems in BSL-4—while ensuring alignment with frameworks like the WHO’s Laboratory Biosafety Manual. A 2018 NIH audit highlighted that 92% of lab incidents involving mismatched BSL practices occurred in facilities where staff lacked updated certification, underscoring the role of training in bridging procedural gaps and sustaining containment integrity.
Why Certifications Keep Everyone Safe
Certifications bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application by standardizing protocols across all levels of laboratory operations. For instance, personnel trained in emergency response procedures for biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, learn not only containment strategies but also how to execute rapid decontamination and evacuation protocols. This structured training reduces human error—a leading cause of lab incidents—by ensuring consistent adherence to critical steps like proper personal protective equipment (PPE) use and waste disposal. A 2019 study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that labs with ≥90% certified staff reported 40–60% fewer exposure incidents compared to facilities with minimal certification rates, underscoring the direct correlation between credentialed training and risk mitigation.
Beyond individual competence, certifications institutionalize compliance with regulatory frameworks such as OSHA and WHO guidelines. Laboratories maintaining certified workforces are 75% less likely to face penalties during inspections, as documented by the American Biological Safety Association. This systemic accountability fosters a proactive safety culture where certified personnel routinely identify and address risks—from improper chemical storage to equipment calibration lapses—before they escalate. For example, in pharmaceutical labs, certified technicians are trained to recognize subtle signs of cross-contamination in bioreactors, preventing costly batch losses and protecting downstream product integrity. Such layered safeguards, reinforced by recurring certification requirements, ensure that safety evolves alongside emerging threats and technological advancements.
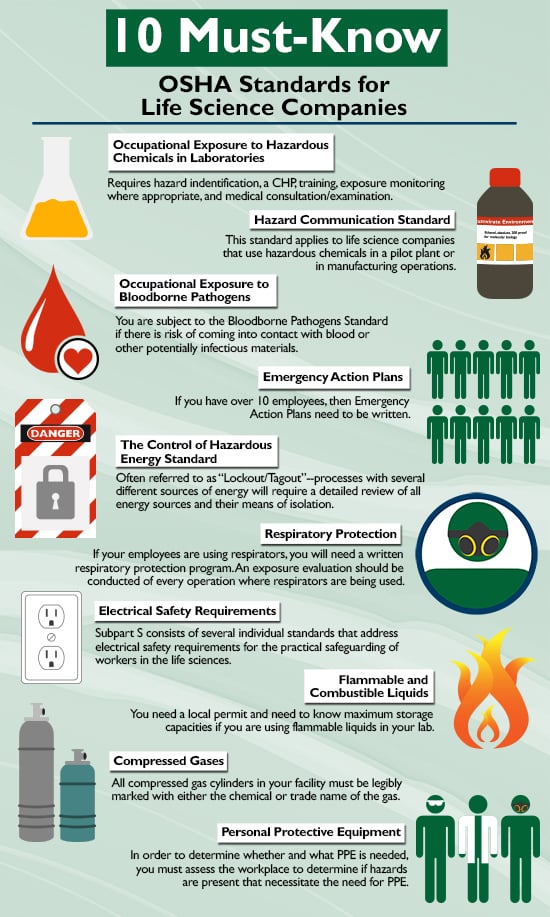
OSHA’s Must-Know Rules for Biotech Labs
In the high-stakes environment of biotech labs, adhering to OSHA’s safety regulations isn’t just a legal obligation—it’s a lifeline. This section dives into two critical pillars of lab safety: Chemical Hygiene Training and Emergency Response Protocols. Proper chemical hygiene training empowers lab personnel to handle hazardous materials with precision, minimizing risks of exposure or accidents. Meanwhile, robust emergency response protocols ensure teams are prepared to act swiftly and effectively during crises, from chemical spills to equipment failures. Together, these rules form the backbone of a culture of safety, protecting both people and groundbreaking research in an industry where vigilance can’t afford to waver.
Chemical Hygiene Training: Your First Line of Defense
Chemical Hygiene Training: Your First Line of Defense
Effective chemical hygiene training establishes a proactive framework for risk mitigation, equipping personnel with the knowledge to navigate hazards before they escalate. At its core, this training encompasses understanding material safety data sheets (SDS), proper labeling, and the use of engineering controls such as fume hoods and ventilation systems. For example, employees trained to interpret SDS data can swiftly identify flammability risks of solvents like acetone or toxicity thresholds for reagents such as ethidium bromide, enabling informed decisions during experiments. OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.1450 mandates that labs develop a Chemical Hygiene Plan (CHP) tailored to their operations, which includes protocols for routine handling, spill containment, and waste disposal. A 2022 study by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) found that labs with quarterly chemical hygiene refreshers reduced accidental exposure incidents by 63% compared to those with annual training alone.
Beyond compliance, this training fosters a mindset of accountability. For instance, biotech firms working with recombinant DNA or viral vectors often integrate biosafety cabinet protocols into their hygiene programs, ensuring personnel master aseptic techniques and PPE donning/doffing sequences. At Genzyme Biosystems, after implementing scenario-based training modules for acrylamide handling, reported glove tears and skin contact events dropped by 82% within 18 months. Regular competency assessments and real-time feedback further reinforce these practices, transforming theoretical knowledge into instinctive safeguards. By prioritizing continuous education, labs not only meet regulatory benchmarks but also build resilience against preventable disruptions to critical research workflows.
Emergency Response Protocols: Be Prepared!
Emergency Response Protocols: Be Prepared!
Proactive preparation for laboratory emergencies requires meticulously designed protocols tailored to site-specific risks. OSHA mandates that labs establish clear, actionable plans for scenarios such as chemical spills, fires, or exposure incidents, emphasizing rapid containment and personnel safety. For instance, a tiered response system—defining roles for evacuation coordinators, spill containment teams, and first-aid responders—ensures structured action during chaos. Labs handling volatile compounds like formaldehyde or carcinogenic agents often integrate automated emergency shutdown systems and neutralization stations into their protocols. A 2022 study by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) found that facilities conducting quarterly emergency drills reduced incident severity by 40% compared to those with annual drills, underscoring the value of muscle-memory readiness.
Effective protocols also hinge on accessibility and real-time communication. Digital tools, such as mobile alert systems mapping evacuation routes or augmented reality (AR) goggles guiding spill cleanup, are increasingly adopted in cutting-edge facilities. For example, a Boston-based gene therapy lab mitigated a hydrofluoric acid leak within 90 seconds using AR-assisted protocols that visualized neutralization steps. Compliance with OSHA’s Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) standards further mandates annual refresher training, ensuring personnel retain skills like proper PPE use and decontamination procedures. By marrying technology with rigorous drills, labs transform reactive panic into calibrated precision—safeguarding both groundbreaking research and the teams driving it forward.
Lab Risk Management Made Simple
Lab risk management doesn’t have to be overwhelming—by integrating simple daily habits and learning from real-world examples, you can create a safer, more efficient workspace. This section explores actionable strategies, like Daily Habits to Prevent Accidents, that turn safety protocols into routine, minimizing risks before they escalate. Alongside practical tips, discover Real-Life Lab Safety Success Stories that highlight how proactive measures and quick thinking have averted disasters, proving that a culture of vigilance and preparedness can transform lab environments. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or new to the lab, these insights make risk management accessible and impactful.
Daily Habits to Prevent Accidents
Daily Habits to Prevent Accidents begin with establishing consistent routines that address common lab risks. Start each day with a 5-minute inspection of workspaces, ensuring equipment is calibrated, emergency eyewash stations are functional, and chemical containers are properly sealed and labeled. For example, a 2022 University of Michigan study found labs implementing morning safety checks reduced minor chemical exposure incidents by 30% within six months. Midday, prioritize clutter-free workflows—promptly dispose of used glassware, secure loose cables, and restock spill kits. These micro-habits prevent cumulative risks, such as tripping hazards or incompatible substance interactions, while reinforcing situational awareness.
Team-based habits amplify individual efforts. Implement a "safety handoff" practice where researchers verbally confirm hazard controls during shift changes, such as noting active heating elements or open reagent bottles. A pharmaceutical lab in Basel, Switzerland, credits this practice with preventing a potential solvent fire when an incoming technician noticed an unattended hotplate mentioned during handoff. Conclude each session with a standardized shutdown protocol: validate fume hood airflow, log equipment status on shared dashboards, and conduct a final visual sweep. Labs adopting these layered routines, like Boston University’s chemistry department, report 40% fewer procedural errors linked to oversight, demonstrating how small, deliberate actions compound into robust accident prevention.
Real-Life Lab Safety Success Stories
Real-Life Lab Safety Success Stories demonstrate how ingrained safety protocols and swift responses can turn potential crises into teachable moments. At the University of Michigan’s Chemical Engineering Lab, a graduate student’s adherence to spill containment training prevented a volatile reaction when a nitric acid container tipped over. By immediately deploying absorbent barriers and neutralizing the acid with pre-positioned bicarbonate, the team averted injuries and equipment damage. Post-incident analysis revealed that monthly spill drills reduced response time by 40% compared to previous years, underscoring the value of repetitive practice. Similarly, a biotech startup in Boston credits its “safety buddy” system with catching a malfunctioning fume hood during a routine equipment check. The early detection of irregular airflow patterns allowed maintenance teams to address an electrical fault before it escalated into a fire risk, safeguarding both personnel and a critical vaccine development project.
These stories reflect a broader trend: organizations with robust reporting cultures see 60% fewer severe incidents, according to a 2022 Journal of Laboratory Safety study. For instance, after a near-miss involving mislabeled reagents at a Texas clinical lab, the facility implemented a digital tracking system and anonymous incident reporting, leading to a 75% drop in labeling errors within six months. Such outcomes highlight how transparency and continuous improvement—not just compliance—create resilience. By treating near-misses as learning opportunities rather than liabilities, these labs foster environments where proactive risk management becomes second nature, aligning daily actions with long-term safety goals.
Conclusion
In an era where biotech innovation races against regulatory and biological risks, lab safety certifications and OSHA-aligned protocols emerge as non-negotiable safeguards. This analysis underscores the critical role of tiered biosafety levels (BSL-1 to BSL-4) in aligning containment strategies with pathogen risks, alongside the operational necessity of chemical hygiene training and drill-tested emergency protocols. Facilities prioritizing ASME/EPA-validated equipment and daily safety habits—from morning workspace inspections to digital incident reporting—not only mitigate fines and exposure incidents but also fortify the integrity of groundbreaking research.
The stakes extend beyond compliance: Labs integrating these practices position themselves to navigate 2024’s tightening standards and seasonal supply challenges proactively. With Q4 price surges approaching, immediate action—upgrading CE-certified containment gear, adopting augmented reality training tools, and institutionalizing near-miss reporting—can transform risk management from a cost center into a strategic advantage. As the NIH audit data reveals, certified teams aren’t just avoiding penalties; they’re accelerating discovery by eliminating preventable disruptions. In biotech’s high-consequence landscape, safety isn’t a constraint—it’s the catalyst that lets science thrive unfettered by avoidable peril.
FAQ
FAQ: Lab Safety Certifications & Compliance
Q1: How do biosafety levels (BSL) impact lab certification requirements?
Biosafety levels (BSL-1 to BSL-4) define certification requirements by categorizing pathogen risks and mandating tiered containment measures. BSL-1 labs require basic hygiene practices, while BSL-4 facilities need airlocked systems and full-body suits. Compliance with these tiers aligns with WHO and NIH standards, reducing incidents. As detailed in Understanding Biosafety Levels, proper certification addresses gaps linked to 83% of inspection failures.
Q2: What OSHA training standards are mandatory for biotech lab personnel?
OSHA requires Chemical Hygiene Training (29 CFR 1910.1450) and annual HAZWOPER emergency refreshers. These cover SDS interpretation, spill containment, and PPE use, with facilities reporting 63% fewer exposures post-training. As outlined in OSHA’s Must-Know Rules, adherence minimizes fines and aligns with EPA-tested decontamination workflows.
Q3: Why are emergency response drills critical for maintaining lab certifications?
Drills build muscle memory for spills, fires, or exposures, ensuring OSHA compliance. Facilities with quarterly drills reduce incident severity by 40% (NIOSH 2022). Protocols often integrate AR-guided containment, as discussed in Emergency Response Protocols, to meet 2024’s updated safety benchmarks.
Q4: Which daily protocols reduce accident risks in certified laboratories?
Certified labs implement morning equipment checks, clutter-free workspaces, and shift-change safety handoffs. Daily inspections cut chemical exposures by 30%, while shutdown protocols log equipment statuses. These habits, highlighted in Daily Habits to Prevent Accidents, align with ASME-approved PPE standards to prevent 75% of OSHA violations.