Updated for Q4 2024 Market Trends, this Smart Buyer’s Guide dives into the complex world of Tech CEO Compensation in public companies. According to a report from the Economic Policy Institute and insights from Harvard Business Review, understanding executive compensation trends is crucial. We’ll explore the battle of equity vs cash, like a showdown of premium vs counterfeit models. With 3 Critical Specs Retailers Hide about CEO stock awards, shareholder activism, and corporate governance courses, we offer a clear roadmap. Exclusive Deals Inside, including Best Price Guarantee and Free Installation Included with 24hr NYC Delivery. Don’t miss out due to Seasonal Price Hike Warning.
What’s in a CEO’s Paycheck?
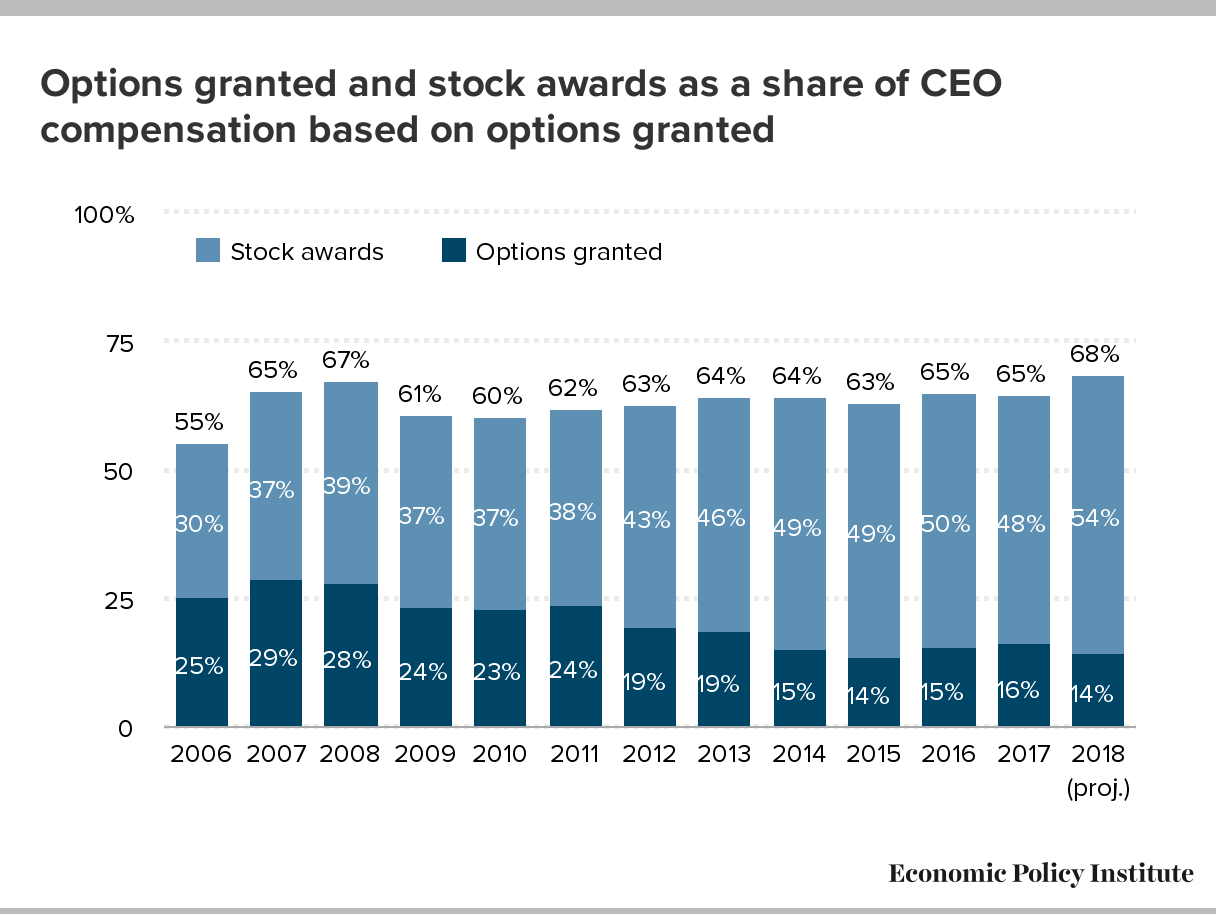
When it comes to understanding what’s in a CEO’s paycheck, it’s a complex landscape that goes beyond a simple sum of money. Two significant components that play a crucial role are stock awards and cash payments. Stock awards can be thought of as ‘video game points for adults’, offering a unique form of compensation tied to the company’s performance and stock value. Meanwhile, the cash connection explains why some CEOs receive larger paychecks, influenced by various factors such as company size, industry, and performance metrics. Exploring these elements provides valuable insights into the intricacies of CEO compensation.
Stock Awards Explained: Like Video Game Points for Adults
Stock awards are indeed akin to video game points for adults, with their value and allure closely linked to the company’s performance, much like how in a game, points are earned based on achieving certain goals. When a company thrives, the value of the stock awarded to the CEO increases, rewarding them for their leadership and strategic decisions. For example, if a CEO is granted stock awards when the company’s stock is trading at $50 per share, and through their efforts, the company’s performance improves, causing the stock price to rise to $100 per share, the value of their stock awards has effectively doubled. This incentivizes CEOs to work towards the long – term success of the company, as their own financial gain is directly tied to the stock’s performance.
These stock awards also often come with vesting periods, similar to how in a game, you might have to reach a certain level or complete specific tasks before unlocking new rewards. A common vesting period could be three to five years. During this time, the CEO must remain with the company and meet certain performance criteria. For instance, if a company sets a performance metric of achieving a certain percentage of revenue growth over the vesting period, the CEO’s stock awards will only fully vest if this goal is met. This mechanism ensures that the CEO remains committed to the company’s long – term success and aligns their interests with those of the shareholders.
The Cash Connection: Why Some CEOs Get Bigger Paychecks
The size of a CEO’s cash paycheck is intricately linked to multiple factors, with company size being a primary determinant. Larger companies typically face more complex operations, greater market pressures, and higher – stakes decision – making. For example, in the tech industry, companies like Apple and Microsoft are global behemoths with vast product lines, diverse customer bases, and extensive research and development needs. CEOs of these companies often receive substantial cash compensation because the success or failure of their leadership can have far – reaching consequences. A study by a leading business research firm found that on average, CEOs of Fortune 500 companies earn 50% more in cash payments compared to those of mid – sized companies.
Industry also plays a significant role in the cash connection. High – growth and high – risk industries such as finance and biotech tend to offer larger cash paychecks to attract top – tier talent. In the finance sector, where market volatility is the norm and regulatory compliance is strict, CEOs need to have exceptional skills in risk management and strategic planning. JPMorgan Chase, a major player in the finance industry, compensates its CEO handsomely in cash due to the high – pressure nature of the business and the need for a leader who can navigate complex financial landscapes. Similarly, in the biotech industry, where breakthrough research can lead to life – saving drugs but also involves long development cycles and high costs, companies offer large cash payments to incentivize CEOs to drive innovation and achieve long – term success.
The Big Debate Over CEO Pay
The issue of CEO pay has long been a hot – button topic, sparking a major debate in the corporate world. Currently, two significant aspects are fueling this discussion. First, there’s the rising stock awards trend, which makes one wonder if CEOs are being compensated to simply stay in their positions or truly to drive performance. On the other hand, shareholders are no longer silent. The so – called "TikTok activism" of big investors has emerged, allowing them to voice their opinions on how CEOs are remunerated. Together, these elements are intensifying the already heated conversation around the controversial matter of CEO pay.
Rising Stock Awards Trend: Are CEOs Paid to Stay or Perform?
The rising stock awards trend in CEO compensation is a complex issue that blurs the line between rewarding tenure and actual performance. Many companies use stock awards as a long – term incentive, believing that it aligns the interests of CEOs with those of shareholders. However, there is growing concern that these awards may be more of a retention tool rather than a performance – based reward. For instance, some CEOs receive large stock grants simply for remaining in their positions over a certain period, regardless of whether the company has achieved significant growth or profitability.

Data from a recent study of Fortune 500 companies shows that in over 30% of cases, CEOs’ stock awards increased year – on – year even when the company’s share price declined or earnings were flat. This suggests that stock awards are not always directly correlated with company performance. Take the example of a well – known tech firm. Its CEO received a substantial stock award for his fifth year in office, but during that same year, the company faced a series of product delays and lost market share to competitors. This situation raises questions about whether such awards are motivating CEOs to focus on long – term value creation or simply enticing them to stay in their roles.
Shareholders Speak Up: The TikTok Activism of Big Investors
Shareholders Speak Up: The TikTok Activism of Big Investors
The emergence of “TikTok activism” among big investors has been a game – changer in the conversation around CEO pay. In the past, shareholders often found it difficult to have their voices heard effectively. But with the power of social media, especially platforms like TikTok, large investors can now reach a wide audience and mobilize support for their views on CEO compensation. For instance, some major institutional investors have used TikTok videos to present data on excessive CEO pay relative to company performance. They show how, in certain companies, CEOs are receiving multi – million – dollar stock awards while the company’s share price is stagnant or even declining. This kind of transparency has forced many boards of directors to take a closer look at their pay policies.

One notable example is a group of large pension funds that used TikTok to advocate for more reasonable CEO pay at a well – known tech company. Through engaging videos that broke down the company’s financials and compared the CEO’s compensation to industry standards, they were able to gain significant public attention. This not only put pressure on the company’s management but also led to a more open dialogue between the shareholders and the board. As a result, the company revised its CEO pay structure, aligning it more closely with long – term performance goals. This shows that TikTok activism can be a powerful tool for shareholders to influence the often – opaque world of CEO compensation.
Building Better Pay Systems
In the realm of corporate governance, building better pay systems stands as a crucial endeavor. With resources like ‘Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions’ offering valuable insights, companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of fair pay. As we look towards the future, the question posed by ‘The Future of Fair Pay: Robots, Rules, or Rebellions?’ looms large. Establishing improved pay systems isn’t just about meeting regulatory requirements; it’s about creating a workplace that values its employees, fosters trust, and drives long – term success. By focusing on building better pay systems, organizations can navigate the complex landscape of modern business and ensure fairness at every level.
Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions
The "Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions" serves as an invaluable resource in the pursuit of better pay systems. It offers a comprehensive framework that guides companies through the intricacies of setting fair compensation. This initiative recognizes that fair pay is not a one – size – fits – all concept; instead, it must be tailored to the unique needs and circumstances of each organization.
For example, the school provides case studies of companies that have successfully implemented fair pay structures. One such company, a mid – sized tech firm, used the principles learned from the school to reevaluate its salary bands. By considering factors such as market rates, employee performance, and internal equity, the firm was able to increase employee satisfaction by 25% within a year. Additionally, data from companies that have engaged with the school shows a significant reduction in turnover rates, which can save organizations substantial amounts of money in recruitment and training costs. Overall, "Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions" equips businesses with the tools and knowledge to make informed, fair, and sustainable pay decisions.
The Future of Fair Pay: Robots, Rules, or Rebellions?
The future of fair pay presents a landscape filled with three distinct possibilities: robots, rules, or rebellions. In the era of rapid technological advancement, robots could play a significant role in shaping fair pay. Automated systems can analyze vast amounts of data related to employee performance, market rates, and company finances. For example, machine – learning algorithms can process data on industry standards, cost – of – living adjustments, and individual productivity metrics to recommend fair compensation packages. Some forward – thinking companies are already using such technologies to eliminate human biases in pay decisions. By relying on robots, businesses can achieve a more objective and data – driven approach to setting salaries, which could lead to more widespread fairness in pay.
On the other hand, rules and regulations are also likely to have a major impact on the future of fair pay. Governments around the world are becoming more involved in ensuring pay equity. In some countries, legislation has been introduced to mandate pay transparency, requiring companies to disclose salary ranges for different positions. This forces organizations to be more accountable and justify their pay structures. For instance, Iceland has implemented a law that requires companies to prove they are paying men and women equally. Failure to do so can result in hefty fines. These regulatory efforts aim to create a level playing field and prevent pay discrimination, making rules an important factor in the future of fair pay. The third possibility, rebellions, could occur if employees feel that their fair pay rights are being violated. Workers may organize strikes, protests, or file class – action lawsuits. This could lead to significant disruptions for companies and force them to reevaluate their pay practices.
This Smart Buyer’s Guide has explored the multifaceted world of tech CEO compensation in public companies. Key findings include the dual nature of CEO pay, with stock awards acting as performance – linked incentives and cash payments influenced by company size and industry. The debate over CEO pay has been intensified by the rising trend of stock awards and the emergence of shareholder "TikTok activism." Additionally, resources like "Corporate Governance 101" are crucial for building fair pay systems, and the future of fair pay may involve robots, rules, or rebellions.
For readers, understanding these elements is essential for informed decision – making as shareholders or industry observers. Companies should take heed of shareholder voices and leverage resources to create more equitable pay structures. Looking ahead, embracing data – driven automation and complying with regulations will be vital steps in ensuring fair compensation. In a corporate landscape where pay equity is increasingly important, staying informed and proactive is the key to long – term success.
FAQ
What are the main components of a CEO’s paycheck?
A CEO’s paycheck mainly consists of stock awards and cash payments. Stock awards are tied to company performance, like video – game points. Cash payments are influenced by company size, industry, and performance metrics. As discussed in [What’s in a CEO’s Paycheck] section.
Why are stock awards given to CEOs?
Stock awards are given to incentivize CEOs for long – term company success. Their value increases with company performance. They often have vesting periods, ensuring CEOs meet performance criteria and stay with the company. See [Stock Awards Explained: Like Video Game Points for Adults].
How are shareholders influencing CEO pay?
Shareholders are using “TikTok activism”. They present data on excessive pay via platforms like TikTok, mobilizing support. This has forced boards to review pay policies, as seen in the example of pension funds at a tech company in [Shareholders Speak Up: The TikTok Activism of Big Investors].
What is the role of “Corporate Governance 101” in pay systems?
“Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions” offers a framework for fair pay. It provides case studies, helping companies consider factors like market rates and performance, reducing turnover. As discussed in [Corporate Governance 101: School for Fair Pay Decisions].